Arizona
Public finance
The governor's budgets are prepared in the Office of Strategic Planning and Budgeting (OSPB). During the 1990's, Arizona moved from an annual to a biennial budget format. Agency requests are submitted to the OSPB by September 1, and agency hearings are held in November and December. The governor's budget is submitted in January, and the legislature is expected to pass the budget in the period January to April.
In 1998, a depressed economy resulted from the Asian crisis and the Russian devaluation, forcing growth in Arizona to drop below 4% for the first time since 1992. In 1999, the economic picture was looking much brighter: the governor of Arizona recommended adjustments to the biennial budget pursuant to increases in revenue attributed to high sales levels and corporate tax collections. General fund revenues for 1999 exceeded projections by almost $100 million, most of which was slated for educational improvements in the state. The governor was also able to reduce tax rates in 2002 for corporations, but not for individuals. However, the recession in 2001 brought a budget crisis in 2002. Medicaid expenditures grew 38.6% in 2001/02 (and by 26.4% in 2002/03, the largest percent increases among the states), exceeding appropriations by $62 million, while revenues came in below projections. A total of $671.2 million was cut from the 2001/02 after it was enacted. Measures taken to close the budget gap in the General Fund included fee increases, layoffs, across-the-board budget cuts, reduced local aid, program reorganizations, infusions from the state's rainy day fund and from other funds. Despite an 8.1% decrease in General Fund appropriations for 2002/03, cuts amounting to $393.6 million were made in state's budget after it was enacted. The budget deficit for 2002/03 was estimated at $500 million (about 8% of the total budget), and for 2003/04 projected at $1 billion (about 15.8%), despite constitutional provisions that require the governor to submit, legislature to pass, and the governor to sign, a balanced budget. Fiscal year 2001 ended with a balance of $409 million, including $373 million in the state's stabilization (rainy day) fund. Fiscal 2002, ended with a balance of $66 million, $65 million in the stabilization fund, and 2002/03 was estimated to end with a $61 million balance, but with the rainy day fund emptied. Fiscal year 2004 was projected to end with a total balance of $2 million, with nothing in the rainy day fund.
The following table from the US Census Bureau contains information on revenues, expenditures, indebtedness, and cash/securities for 2001.
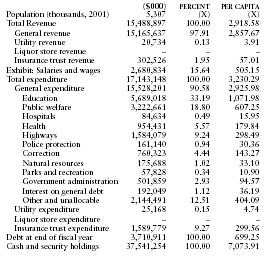
| ($000) | PERCENT | PER CAPITA | |
| Population (thousands, 2001) | 5,307 | (X) | (X) |
| Total Revenue | 15,488,897 | 100.00 | 2,918.58 |
| General revenue | 15,165,637 | 97.91 | 2,857.67 |
| Utility revenue | 20,734 | 0.13 | 3.91 |
| Liquor store revenue | – | – | – |
| Insurance trust revenue | 302,526 | 1.95 | 57.01 |
| Exhibit: Salaries and wages | 2,680,834 | 15.64 | 505.15 |
| Total expenditure | 17,143,148 | 100.00 | 3,230.29 |
| General expenditure | 15,528,201 | 90.58 | 2,925.98 |
| Education | 5,689,018 | 33.19 | 1,071.98 |
| Public welfare | 3,222,661 | 18.80 | 607.25 |
| Hospitals | 84,634 | 0.49 | 15.95 |
| Health | 954,431 | 5.57 | 179.84 |
| Highways | 1,584,079 | 9.24 | 298.49 |
| Police protection | 161,140 | 0.94 | 30.36 |
| Correction | 760,323 | 4.44 | 143.27 |
| Natural resources | 175,688 | 1.02 | 33.10 |
| Parks and recreation | 57,828 | 0.34 | 10.90 |
| Government administration | 501,859 | 2.93 | 94.57 |
| Interest on general debt | 192,049 | 1.12 | 36.19 |
| Other and unallocable | 2,144,491 | 12.51 | 404.09 |
| Utility expenditure | 25,168 | 0.15 | 4.74 |
| Liquor store expenditure | – | – | – |
| Insurance trust expenditure | 1,589,779 | 9.27 | 299.56 |
| Debt at end of fiscal year | 3,710,911 | 100.00 | 699.25 |
| Cash and security holdings | 37,541,254 | 100.00 | 7,073.91 |